April 08, 2024
AAA – Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
A general framework for controlling accessibility to data on computer systems, enforcing security and control policies, auditing usage, and providing the information necessary for all accountability for access and usage. These combined processes, when applied, are important for effective and safe network management and overall security.
AC – Active Content
Program code embedded in a web page and when page is accessed the embedded code is automatically down loaded and executed on the user’s browser.
ACL – Access Control List
A set of rules that either allow access to a computer, the data therein, and or all the associated data environment. It is also a set of rules that denies all or partial access.
There are two types of ACL’s generally:
- Filesystem ACLs: Filters that manage access to directories or files in a computer system. A filesystem ACL gives the operating system instructions as to the users that are allowed to access the system, as well as the access and data privileges they are entitled to once they are inside.
- Networking ACLs: Networking ACL’s manage access to a network. This provides instructions to switches and routers as to the kinds of traffic and devices that the user can be allowed to interface within the network.
AI – Artificial Intelligence
The latest term originally from Dartmouth College as far back as 1956 is defined as “the construction of computer programs that engage in tasks that are currently more satisfactorily performed by human beings because they require high-level mental processes such as perceptual learning, memory organization, and critical reasoning.”
AES – Advanced Encryption Standard
NIST encryption standard for unclassified and publicly disclosed encryption standard algorithm.
AMTD – Automated Moving Target Defense
(also see MTD) The automated concept of controlling change across multiple system dimensions in order to increase uncertainty of targets, change the attack surfaces and increase apparent complexity for attackers, to reduce their window of opportunity, change target visibility and increase the time costs of their probing and attack efforts. This also helps expose attack attempts and methods.
APT – Advanced Persistent Threat
An organized cyberattack by a group of skilled, sophisticated threat actors. APTs are not “hit and run” attacks. Attackers plan their campaigns carefully against strategic targets and carry them out over a prolonged period of time. APTs are compound attacks involving multiple stages and a variety of attack techniques. Many common attack vectors were initially introduced as parts of an APT campaign with zero-day exploits and malware, customized credential theft, and lateral movement tools as the most prominent examples. APT campaigns tend to involve multiple attack patterns and multiple access points.
APT attacker goals, and consequences faced by organizations, include:
- Theft of intellectual property
- Theft of classified data
- Theft of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) or other sensitive data like Health (PHI) or credit (PCI) information!
- Sabotage, for example, database deletion or Encryption (see Ransomware)
- Complete site takeover
- Obtaining data on infrastructure for reconnaissance purposes
- Obtaining credentials to critical systems
- Access to sensitive or incriminating communications
ARP – Address Resolution Protocol
ARP translates the software address (IP address) to the physical address (MAC address when a computing device is on a network) of every host connected to the network. Applications and software connected to the Internet use IP addresses to send information. Meanwhile, the communication between systems happens through hardware addresses, also known as MAC or physical addresses. Without ARP, software and devices would not be able to send data to each other.
AVG – Average Virtual Gateway
Used in Cisco’s GLPB proprietary solution for load balancing and redundancy in the network. Only one AVG is available in each GLPB group and it’s responsible for replying (Plus assigning) the local MAC addresses to the initial ARP requests for the Virtual IP address (VIP). AVG assigns a different virtual MAC address to the Active Virtual Forwarders (AVFs). This is done when the AVG replies to the initial ARP request from the group host. ARP replies are unicast and are not heard by other hosts on the same broadcast segment. AVF is responsible for the routing traffic received from assigned hosts. The host may use the same virtual MAC address of an AVF, as long as it stays reachable with no timeout.
AWS EFS
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic File System (EFS) – this is a cloud-based file storage service that offers scalable, elastic, and secure file storage for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. It is designed to provide a simple, scalable, fully managed elastic NFS file system for use with AWS cloud services and on-premises resources. AWS EFS is built to be highly available and durable, automatically replicating your data within a region to protect against data loss.
AX
Analyst Experience – In today’s competitive environment it is essential to continuously improve the analyst experience in order to maximize your security team’s efficiency as they protect the organization’s data environment. It is essential to focus on what matters the most in the security analysts’ environment to make their jobs easier and also to reduce burnout to help retain their top talent.
AZ
Availability Zones – In the cloud these are resources, like memory or storage resources for applications and/or data usage to act either as a backup area or for work offload and/or as a singular application offset area. These zones may also be used for Backup in disaster recovery modalities.
BaaS – Backend as a Service
BaaS allows developers to focus on the front-end of their applications and leverage back-end services and applications without building or maintaining them. BaaS and serverless computing share some similarities but are not the same.
BCP – Business Continuity Plan
BCP is the plan every business should have for emergency backup operations and post-disaster recovery to ensure the availability of critical resources to provide continuity of business operations! This should be a DRP – Disaster Recovery Plan!
BDPU – Bridge Data Protocol Unit
BaaS allows developers to focus on the front-end of their applications and leverage back-end services and applications without building or maintaining them. BaaS and serverless computing share some similarities but are not the same.
BEC – Business Email Compromise
BEC is a type of cyberattack where financially motivated bad actors/hackers trick unsuspecting executives and employees into sending money or sensitive data to fraudulent accounts usually using a hacked email.
BGP – Border Gateway Protocol
BGP is the protocol that enables the global data packet routing system of the Internet. It manages how packets get routed from network to network by exchanging routing (like your GPS routes used to reach a physical destination) and reachability information among edge network routers of autonomous systems (AS). Attributes that may include: Highest weight/value, Current reachability, hop counts (if set), local router preferences, time-to-live settings, and oldest path are considered. BGP networking is based on the TCP/IP model at Layer 4 (in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI Model)) to control the network layer (Layer 3 – the Internet layer) inter-network communications. In essence, BGP provides connectivity information that can be used to derive Internet packet forwarding tables that help to route packets to their correct destinations.
BooTP – Bootstrap Protocol
BooTP protocol was used by a configuration server to automatically assign an IP address to a network device. Parts of BooTP have been superseded by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). BooTP it is still used today even though it was originally released in 1985 to replace RARP! When a computer boots up it sends BooTP broadcasts out to get its IP address assignment. You will see BooTP, UDP, and DHCP activity on ports 67 and 68.
BS-99 – British Standard 7799
BS-99 a British standard also ISO-27001 guides how to secure a networked data system. It includes the recommended management framework, the objectives, and Data control requirements for an (ISMS) Information Security Management System.
BSSID – Basic Service Set Identifier
BSSID stands for Basic Service Set Identifier, and it’s the MAC physical address of the access point or wireless router that is used to connect to the WiFi.
CaaS – Container as a Service
CaaS is a category of cloud services where the service provider offers customers the ability to manage and deploy containerized applications and clusters. CaaS is sometimes viewed as a special sub-type of the infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) cloud service delivery model, but where the main commodity is containers rather than physical hardware and virtual machines.
CAC – Call Admission Control
CAC is the standard for inspection and control of all inbound and outbound voice digital network (VoIP) activity by a voice firewall (possibly a DPI Server) based on corporate and user-defined access and control policies.
CASB – Cloud Access Security Broker
An on-premises, or cloud-based security policy enforcement point, is placed between cloud service consumers and cloud service providers to combine and interject enterprise security policies. This handles multiple types of security policy enforcement. Security policies may include authentication, single sign-on, basic authorization, access levels, credential and usage mapping, device profiling/types, encryption, tokenization, logging, alerting, malware detection/prevention, etc…
CAPES – Cloud-native, API-enabled Email Security
CAPES is a Forrester term. These are solutions that integrate with email infrastructure providers like Google and Microsoft to extend their native security capabilities and catch malicious and fraudulent emails those systems may have missed.
CAVP – Cryptographic Algorithm Validation Program
CAVP is a NIST program that provides validation testing of NIST-recommended cryptographic data algorithms and related components. These encryption algorithms are also approved by the National Voluntary Laboratory Accreditation Program as well as other accredited Cryptographic and Security Testing (CST) Laboratories that test and verify algorithm security implementations. Once the algorithm is approved it is added to a Validation List which identifies the vendor, implementation, operational environment, validation date, and algorithm details. These programs are very important in understanding and usage of the various methods and standards that ensure secure data encryption.
CDN – Content Delivery Network
CDNs are formalized content cache systems that are used to deliver content to users efficiently and as locally as possible. A CDN may be used, for example, to deliver streaming video services. This is a physical or virtual network focused on delivering every network event that has any content we use. The CDNs are invisible but make sure everything we do is delivered.
CDP – Cisco Discovery Protocol
A unique Cisco proprietary data link layer (layer 2 of the OSI) protocol that helps with Cisco device inventory. CDP runs between direct/physically connected Cisco network entities (routers, switches, remote access devices, IP telephones, etc.) to supply an inventory of devices with information about their direct connected neighbors.
CERT – Computer Emergency Response Team
CERT the Team that will provide incident response services to victims of attacks including vulnerabilities and other threats. The CERT Team may be internal or external and may also offer more information to help improve overall network security.
CDR – Content Disarm and Reconstruction
CDR proactively protects end-users from potentially dangerous content by deleting executable content. CDR is also known as Threat Extraction. This is a unique method of protection as it does not rely on detection visibility like other security-focused solutions as it deletes all active content included.
CHAP – Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
A routine that prevents Recall or Replay Attacks by a challenge/response authentication mechanism where the response required varies with every challenge.
CI/CD – Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment
In the Cloud services, the methods for the orchestration of custom data buckets and control of content delivery networks (CDNs).
CIDR – Classless Inter-Domain Routing
Sometimes called Super Netting, CIDR performs the task of subnetting, which saves a lot of IP addresses. CIDR makes networks more efficient and helps delay the exhaustion of the IPv4 address system. It is a method for saving IP addresses in delivering content. Addresses are not bound by class; CIDR can organize IP addresses into subnets and that saves wasting many IP addresses!
CISA – Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency
CISA is a U.S. Government agency and is the leader and repository of national risk management for cyber and physical infrastructure for Product Issues, Vulnerabilities as well as attacks. Also, through information sharing, deployment of detective and preventative technologies, and providing incident response and “hunt” capabilities to minimize impacts of identified incidents and or vulnerabilities.
CISO – Chief Information Security Officer
A senior-level executive who oversees the implementation and development of the organization’s information, cyber, and network security. The CISO’s responsibilities include developing a Network Security Team to help develop, implement, and enforce network and security policies that will protect the corporation’s critical (Corporate Gold) DATA!
Cloud
The term “cloud” refers to a network of remote servers that are accessed over the Internet to store, manage, and process data. It provides on-demand computing resources and services, such as storage, applications, and infrastructure, without requiring direct user management or physical presence. Some say this is the most dangerous data storage today!
CS – Cyber Security
The name and practices needed to protect computer systems, networks (physical, virtual and or hard), and corporate and protected data from unauthorized access, attacks, and damage. It involves implementing rules and technology measures to ensure access control, confidentiality, integrity, availability, protection and resilience of digital assets. Sometimes called Data Security, Network Security, etc.
CSPM – Cloud Security Posture Management
A cloud-focused arena is a segment for security tools designed to identify misconfiguration issues and compliance risks in the cloud. CSPM helps continuously monitor cloud infrastructure for gaps in security policy enforcement. Gartner coined the term and described CSPM as a category of security products that help automate security and provide compliance assurance in the cloud. CSPM is used by organizations that have adopted a cloud-first strategy and want to extend their security best practices to hybrid cloud and multi-cloud environments. While CSPM is mostly associated with IaaS, the technology can also be used to minimize configuration mistakes and reduce compliance risks in SaaS and PaaS environments.
CTI – Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber Threat Intelligence comes from these and other areas: malware signatures, known-bad IP addresses, domain names, and information about current cyberattack campaigns. The idea is to help prevent attacks from learning from previous attacks and intelligence from resources like CISA..etc
CVE – Common Vulnerabilities and Exposure
CVE is a list of publicly disclosed information security vulnerabilities and exposures. It was launched in 1999 by the MITRE corporation to identify and categorize vulnerabilities in software and firmware. Authorities like CISA will assign a CVE ID designator to a newly discovered vulnerability to make it easier to track and collate.
DDoS – Distributed Denial-of-Service
A Distributed Network Attack is designed to exploit the limits of a network to prevent the company, etc. from carrying out business functions and capabilities. It is a data flood attack to overcome the ability of targeted networks to respond to legitimate requests, services and normal business.
DDoS DPI – Deep Packet Inspection
For Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks – DDoS DPI equipment and services can help block several types and causes of a DDOS attack and resulting network issues. DPI in general is a way to reveal malware as it enters the network and with regards to DDOS attacks, can detect worms as they try to get into networks, as well as detecting IoT/IIoT inside attacks.
DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
This protocol helps automate the process of configuring devices for communications on an IP network by automatically assigning an IP addresses and other required communication parameters to devices being connected to the network using a client-server architecture and using network services, such as Domain Name Services (DNS), Network Time Protocol (NTP), and any communication protocol based on UDP or TCP. It has superseded BooTP, but BooTP is still used in the computer boot process. One can see the DHCP negotiations on ports 67 and 68.
DLP – Data Loss Prevention
DLP is the practice (sometimes theoretically) of establishing rules set for detecting and preventing data breaches or exfiltration or unwanted destruction or encryption and leakage of sensitive data of all kinds from corporate to medical data! This is the fundamental of Network Data Security practices!
DMARC – Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance
This is an email authentication protocol! It is designed to helps domain administrators protect their domain from unauthorized use, commonly known as email spoofing!
DMVPN – Dynamic Multipoint VPN
An application that allows data exchanges on a secure network without the use of a central VPN server or router. This creates a mesh VPN protocol that can be applied selectively to connections or spokes being utilized in the business concurrently. Each different site (or spoke) can connect to one another securely without individual setups.
DMZ – Demilitarized Zone
DMZ’s help via a layered security model as they provide a subnetwork segmentation based on corporate security policies. They also can provide either a transit mechanism from a secure source to an insecure destination or from an insecure source to a secure destination. In any case they act as a standoff system to provide for a more secure access model.
DNS – Domain Name System
A system that translates domain names into IP addresses that browsers and other Internet applications use to load Internet pages, etc. providing viewer access/visibility. One needs an address to send Mail or Data too.
DPC – Deep Packet Content
DPC refers to the payload of packets at different layers of the Internet protocol stack. It involves inspecting the payload, including text, files, or multimedia data, to extract specific information, apply content-based filtering or policies, and perform deep-level analysis for various purposes, such as content filtering, data loss prevention, or compliance monitoring.
DPI – Deep Packet Inspection
A network monitoring and filtering technique that examines the contents of data packets to layer 7. It allows for granular analysis of packet headers and payloads to gain insight into network traffic, detect specific applications or protocols, and identify potential security threats or policy violations.
Please Note: Following are several different advanced and focused DPI devices and methods to protect the network in different places and in many different areas. This information should be self-explanatory:
DPI-AS – Deep Packet Inspection for Autonomous Systems (network routing and management)
DPI-DNS – Deep Packet Inspection for Domain Name System traffic
DPI – Deep Packet Inspection for Enhanced Traffic Intelligence – 5G network slicing
DPI-FTP – Deep Packet Inspection for File Transfer Protocol traffic
DPI-HTTP – Deep Packet Inspection for Hypertext Transfer Protocol traffic
DPI-IM – Deep Packet Inspection for Instant Messaging traffic
DPI-POP3 – Deep Packet Inspection for Post Office Protocol version 3 traffic
DPI-RTSP – Deep Packet Inspection for Real-Time Streaming Protocol traffic
DPI-SIP – Deep Packet Inspection for Session Initiation Protocol traffic
DPI-SMTP – Deep Packet Inspection for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol traffic
DPI-SSH – Deep Packet Inspection for Secure Shell traffic
DPI-VPN – Deep Packet Inspection for Virtual Private Networks
DNPI – Directorate of Industrial Property-Uruguay, Spain
Under the Ministry of Industry, Energy and Mining which is aligned with the EURO-CP-5.- New public platform for Trademarks and Patents.
DRaaS – Disaster Recovery as a Service
A third-party cloud service provides for restoration of corrupted data or disaster recovery of all kinds, including Ransomware remediation.
DSCP – Differentiated Services Code Point
A part of the Quality-of-Service configuration on routers is the Differentiated Services (DiffServ) field. The six most significant bits of the DiffServ 8 bits are the DSCP field for classifying and managing data traffic and providing QoS standards required. DSCP can provide for low latency for important data and best effort for other non-critical data flows. DSCP replaces the older Type of Service (ToS).
EDR – Endpoint Detection and Response
A cybersecurity technology, also known as ETDR – Endpoint Threat Detection and Response, is mainly focused on endpoint continuous monitoring looking for aberrant behavior for threat detection and alerts.
EGP – Exterior Gateway Protocol
An older generic protocol is/was used to exchange reachability between Internet gateways to different systems. EGP was originally use by ARPANET but is no longer popular and was replaced by BGP and other advanced protocols.
EIGRP – Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
Enhanced Cisco version of IGRP and BGP “Routing table with shortest path information” allows routers to exchange network and management informational changes much faster. Using only Hello packets for normal routing operation with quick changes updates with only the needed information not the entire route table and using the enhanced Diffused Update Algorithm for quicker and more accurate shortest path calculations.
EPP – Endpoint Protection Platform
A suite of different technologies designed to protect an organization’s infrastructure and data by monitoring and recognizing known threats, such as traditional malware and even unknown threats. EPP is a major part is EPDR (Endpoint Protection Detection and Response) that continuously monitors endpoints to classify 100% of processes before and after execution to detect and respond to attacks and in-memory exploits automatically. An EPDR system reveals and blocks the strange behaviors of users, machines, and processes while proactively discovering new hacking and growing its knowledge of evasion techniques and tactics.
ESG – Environment, Social and Governance
A set of standards for a company’s behavior used by socially conscious investors to screen potential investments. Businesses taking up the ESG cause pledge to be ethically bound in how they treat their people and customers with respect, have a strict set of boundaries when it comes to policy making and consider the environmental implications of not only their own actions but how it effects their Internet posture!
ETP – Email Threat Protection
There are two locations for ETP deployment – On-Premise or Cloud Based – Today’s emails are vulnerable to cyber-attacks of many kinds with variable malicious content! ETP is designed to identify threats like aberrant access and to stop email-borne attacks which include SPAM, phishing (i.e. Whaling, Smishing), ransomware, deceptive content (i.e. Invoices, order documents), and many other exploitable message content that is sent in an email body or downloaded as an email attachment or web link. This is extremely important with Cloud and SaaS deployments.
FaaS – Function as a Service
An advanced cloud service providing customers with a platform to develop service-oriented applications where they may test, run, and manage their applications. The costs are similar to other “X”aaS services which are charged on the actual run-time of the services and functions are run.
FDC – Fault Detection and Classification
This is to detect abnormal behavior and classified for administrative review and security review.
FIM – File Integrity Monitoring
A technique where certain files and or logs are monitored for any file changes or modifications. If any changes are detected, alerts are sent to security personnel for review and actions. Changes could indicate a breach or hacking.
FWaaS – FireWall as a Service
A cloud-based service that provides hyperscale, next-generation firewall (NGFW) capabilities, which may include web filtering and other advanced threat protection services.
GLBP – Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
A Cisco round-robin load balancing protocol that protects data traffic from a failed router or circuit, like the Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), which allows for packet load sharing between a group of redundant routers (tables)/gateways using a virtual gateway (AVG-Average Virtual Gateway) to manage the load distribution for each member using a virtual MAC address.
GRC – Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance
A set of policies, rules, and the framework that a company will use to achieve its business goals while protecting (Security) its network and the data within (i.e. HIPPA, PCI..etc). It defines the responsibilities of key stakeholders, such as the board of directors and senior management i.e. CISO. This is necessary for good corporate governance which must support your network team! GRC also includes the company’s Social and Legal responsibilities and its policies for Data Protection, Mitigation, and Recovery.
GRE – Generic Routing Encapsulation
A packet tunneling protocol originally created by Cisco for encapsulating data packets that use one routing protocol inside the packets of another protocol.
GTP – GPRS Tunneling Protocol
General Packet Radio Services is a protocol to allow data network, and Internet transmission of data (IPv4, IPv6, PPP packets) from the cell domain and other radio services, including GSM, UMTS, LTE and 5G NR and other radio networks. There are 3 basic standards to provide for these services – GTP-C, GPT-U and GTP’ (prime).
HAN – Health Alert Network
A network for the CDC and other health organizations to communicate urgent health alerts, messages and information to WWW and local agencies, as well as to the public.
HSRP – Hot Standby Router Protocol
One of the two most popular Cisco router redundancy protocols. The other is VRRP – Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol. This Cisco protocol allows a network to have two or more routers for backup/redundancy while giving the network the illusion of just one router where only one router is active at a time.
HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol
An application layer protocol that is an essential part of the WWW that links us through webpages.
HTTPS – Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
The secure/encrypted (public and SSL encryption) version of HTTP.
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
One of three types of cloud-as-a-service options (see PaaS, SaaS) which offers computing, storage and networking services on a demand-as-needed basis. Sometimes, corporation need more network functionality and IaaS can provide as-needed and pay-as-needed.
IAM – Identity and Access Management
A “MUST” business security discipline that enables the right people, software, and hardware to have access to only the authorized tools required to perform their duties. These procedures prevent granting them access to functions that present a security risk to the corporate network.
ICMP – Internet Control Message Protocol
An error-reporting protocol that network devices, such as routers, intermediary devices and hosts, use to communicate error information or updates to other routers or hosts and is used to generate error messages to the source IP address when network problems prevent delivery of IP data packets. ICMP creates and sends messages to the source IP address indicating that a gateway to the Internet, such as a router, service or host, cannot be reached for packet delivery. ICMP can also be used to troubleshoot Internet connections using ping and traceroute functions.
ICS – Incident Command System
A standardized method of command, control, and coordination of emergency response provides a common hierarchy within which responders from multiple agencies or departments work together to control all issues effectively and quickly. i.e. A major breach in the supply chain, many groups will work together to stop the attack and the effects that the attack has caused!
ICS – Internet Connection Sharing
This Windows service enables one Internet-connected computer to share its Internet connection with other computers on a local area network (LAN).
IDF – Intermediate Distribution Frame
A rack-mounted cable distribution solution. It is a physical rack used for mounting network and telecommunications equipment.
IDS – Intrusion Detection System (often used in conjunction with DPI)
A hardware and software device/solution or set of devices used to detect an intrusion or vulnerability exploits against a target application or network.
IEEE – The Institute for Electrical Electronic Engineers
A highly prestigious professional organization. The IEEE is dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. There are 3 levels of professional membership (400, 000 members in 160 countries) other than student level – Member, Senior, and Fellow.
IEEE SA
The standards part of the IEEE, where standards/recommendations are written and collective technology is shared.
IGMP – Internet Group Management Protocol
There are two types of IGMP – V1 and V2. This is a protocol that allows several devices to share one IP address so they can all receive the same data broadcast. IGMP is an IPv4 network layer protocol used to set up multicasting on networks, which allows and manages the devices to join or leave the multicast group membership and is not a multicast routing protocol.
IGP – Interior Gateway Protocol
There are two categories of IP routing protocols: Interior gateway protocol (IGP) and Exterior gateway protocol (EGP). If the routing protocol is designed to be used in a single autonomous system, it comes under the IGP definition. If a routing protocol is designed and intended to be used in between different (2 or more) autonomous systems, it comes under the EGP definition.
IMAP – Internet Message Access Protocol
A standard email retrieval (incoming) protocol. It allows email messages to be stored on a mail server and allows the recipient to view and manipulate them as though they were stored locally on their computers or other devices.
IoT – Internet of Things
Physical objects/devices embedded with sensors and actuators that communicate with and through computing networks which allows the physical world like temperature, pressure, etc., to be digitally monitored and or controlled.
IIoT – Industrial Internet of Things
This refers to network-connected manufacturing control devices and applications to automate, optimize, and manage industrial processes like manufacturing, transportation, automobile control, health devices, and utility management.
IP – Internet Protocol
The protocol that supports data to be sent from one computer to another without being directly connected. IP is protocol that defines the modern Internet.
IPS – Intrusion Prevention System (often used in conjunction with DPI)
These systems fall into one of three categories: Host Based Intrusion Detection Systems (HIDS), Network Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS), and a combination of the two. Sometimes IPS is called IDPS, which is Intrusion Detection Prevention System. These both are designed to monitor a network for any known malicious activities or activity that is attempting to exploit a known vulnerability.
These systems can do many things to mitigate attacks or intrusions including:
- Sending an alarm and report notification to the administrator
- Dropping the malicious packets
- Blocking traffic from the source address
- Resetting the connection
- Help in configuring firewalls to prevent future attacks
IPSec – Internet Protocol Security
A set of communication rules/protocols to set up secure connections over a network. Internet Protocol (IP) is the common standard that determines how data travels over the Internet. IP sec adds encryption and authentication to secure the connection and data sent.
IPSec VPN – Internet Protocol Security VPN
Where the IPSec protocol is used to create encrypted tunnels through the Internet. It provides end-to-end encryption, which means data is scrambled at the sending computer and unscrambled at the receiving server
ISACA – Information Systems Audit and Control Association
A professional organization committed to the advancement of digital trust by empowering IS/IT professionals to grow their skills and knowledge in audit, cybersecurity, emerging tech and more. Members get personalized training, and educational resources and can earn the most in-demand credentials—all backed by the support of industry-leading IT experts from around the world. Their CISA (Certified Information Systems Auditor) and CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) Plus many more certifications are highly recognized as industry standards!
ISP – Internet Service Provider
A company that provides access to the Internet to homes and businesses.
ITAM –Information Technology Asset Management (ITAM)
ITAM is the management process of full-cycle care of the corporation’s/organization’s business data assets. The ITAM process fully accounts for one’s data cycle from original deployment, maintenance, upgraded legally (i.e., Credit card, personal information…etc.) as needed and at the end of value cycle full protection against retrieval and total disposal of the data. This cycle may be mandated by law (i.e., GDPR, State, Federal and country laws) or the lack of business value,
ITDR – Identity Threat Detection and Response
Gartner defines ITDR as “a security discipline that encompasses threat intelligence – with best practices, a knowledge base, tools, and processes to protect identity systems. It works by implementing detection mechanisms, investigating suspicious posture changes and activities, and responding to attacks to restore the integrity of the identity infrastructure.”
LAN – Local Area Network
This is a group of computing devices that are connected in one physical location. LANs can be simply a home network for very large users like colleges or businesses.
L2TP – Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
An extension of the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) used by Internet service providers to enable virtual private networks (VPNs) to ensure security and privacy of the data transported.
L7 DPI – Layer 7 Deep Packet Inspection
Deep Packet Inspection of all Layer 7 data.
LACP – Link Aggregation Control Protocol
IEEE 802.3ad standard that allows the user to combine numerous physical Ethernet links into one logical link, allows multiple ports collectively as a single channel or multiple physical ports as one port.
LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
LDAP has two main goals: 1) to store data in the LDAP directory and 2) to authenticate users to allow access to the directory. LDAP servers store the identity data for authenticating users to use an application or access to user data.
LLM – Large Language Models
Specialized Machine Learning algorithms that model languages for the purposes of language output generation. Sometimes referred to as Generative AI.
LOS – Line of Sight
Where one can see from their position physically or from their access point in a network. Also, line of sight refers to the ability of a transmitter to literally see the receiver or vice-versa. It is not specific to access points.
MAC – Media (or Medium) Access Control
This layer 2 network policy is for data transfer that regulates how data is transmitted between two computing devices. MAC refers to pretty much any layer 2 access method, not just Ethernet, for example. MACs are conventions for media access control that incorporate rules for device transmission and reception.
The MAC protocol tries to ensure the non-collision of data being transferred between two computer/network devices. Data collisions are not good and can disrupt overall communications.
MAF – A Multi-Access Function
A cyber security access protocol to secure access requiring more than one action to log in or get access to a network or data function.
MAN – Metropolitan Area Network
There are two types on MANS – hard and wireless (WMAN). Both are located in a local, but wider than one building area where they can communicate without intervention of another carrier. A campus wide network is the best example. This is usually within a 5-to-10-mile (or so) area, but directly connected.
MBaaS – Mobile Backend-as-a-Service
A mobile access method to the cloud used by programmers and developers using specific and standard Application Programming Interfaces (APIs)(I.e. Android/iOS) and Software Development Kits (SDK’s), which help in lowering costs, but raises hackability. This allows organizations that want to utilize off-premise servers to use MBaaS to connect their application’s backend access resources.
MDF – Main Distribution Frame
The main demarcation point between the internal network and the external transport or WAN domain. If one is going from the inside network (LANS) to the outside network (WANS) they probably have an MDF. Inside physically segmented networks there can be a LAN distribution panel or Frame.
MDP – Markov Decision Process
A rules-based decision process used for automation decision making for data and network tools, i.e. with smart tools like Firewalls, DPI, DCM, SIEMs, IoT, IIoT, etc. which use these smart algorithms for establishing rules for passing or deleting data packets and recognition of aberrant activity.
MDR – Managed Detection and Response
Estimates believe 60% of organizations will be actively using remote threat disruption and containment capabilities delivered as MDR. However, a specific definition has NOT been established. Gartner coined the phrase in 2016 which defines MDR as where a vendor provides customers with remotely delivered, human-led SOC functions for the purposes of incident reporting, rapid detection, analysis, and investigation of threats, as well as remote mitigative responses to those threats. Services may be added or subtracted as required.
MFA – Multi-Function Authentication
MFA is an access security method that requires two or more verification inputs to access an account, file, or system. This security method involves a unique digital code or key separate from your password and operates like a secret passphrase or fingerprint to verify your identity. One method is codes sent to email or cell devices like phones as a txt message.
MIMO – Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
This wireless technology uses multiple transmit and receive antennas, which are simultaneously used for transmission and reception, allowing increased data channel capacity. MIMO uses the spatial frequency diversity present in the standard WiFi, cellular or direct RF modulation techniques present in the channels between multiple transmit and receive antenna pairs.
MIMO is designed to provide high data rate with reliable communications to a large number of wireless terminals using a shared wireless (RF) medium like antennas using a multiple access channel (MAC – NOT Medium Access Control) such as in the cellular arena.
There are several versions of MIMO – i.e. MIMO-OFDMA Terahertz for IoT and IIoT networks often called THz MIMO OFDM for THz level transmission modulation method called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) systems, MU-MIMO – Multi User-MIMO, MIMO (IRS) Intelligent Reflecting Surface that uses two effective solutions for compensating the large path loss in THz (6Ghz up) radio systems.
Other variants are – Sequential Parametric
These include Convex Approximation (SPCA), Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer (SWIPT) for advanced power and control methods, and others that identify the different modulation and beam forming types for higher speed control of IoT and IIoT applications including power control.
MPLS – Multi-Protocol Label Switching
This layer 2.5 IP protocol uses Labels rather than regular Router tables to get unique encrypted data to only the receiving user it is assigned to and much faster. Kind of like a VPN! The MPLS header is added to the packet that lies between layers 2 and 3, thus a 2.5-layer protocol. This is much faster than reading long router tables.
MPLS DPI – Deep Packet Inspection for Multi-Protocol Label Switching Networks
This is another of the many DPI applications that read into network MPLS data to find aberrant behavior, dangerous data, dangerous outside addresses, bad paths, aberrant connections, etc.
MSP – Managed Service Provider
External services to monitor and protect your network and data.
MSTP – Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
The IEEE 802.1’s standard that allows a single physical network switch to support multiple spanning-tree connecting instances. This is very useful for companies with lots of VLANs in the network and wants to communicate with separate spanning-tree instances for different groups of VLANs.
MTD – Moving Target Defense
See AMTD above.
MTU – Maximum Transmission Unit
Sets the largest packet (PDU) size, specified in octets (eight-bit bytes –Two nibbles- even though ASCII only uses the first 7 of the bits) that can be sent in a TCP packet or frame per transmission. There is just under 4Gb in an IPv6 JumboGram. There are different MTU’s for different transport modes, like IPv4 versus IPv6, versus WiFi versus Ethernet Jumbo Frames, etc. Ethernet has a minimum frame size of 64 bytes, comprising an 18-byte header and a payload of 46 bytes. It also has a maximum frame size of 1518 bytes; in which case the payload is 1500 bytes.
NAC – Network Access Control
This rules-based security solution uses unique access protocols to keep unauthorized users and devices out of a private network. These also give restricted access to the devices, which are compliant with network security policies. It is sometimes known as Network Admission Control. It handles network management and security that implements security policy, compliance, and management of access control to a network. These software rules, along with DPI and other hard security devices, can help keep a network safe, but NAC alone is NOT sufficient to fully protect a network.
NAS – Network Attached Storage
Centralized network devices (i.e., hard drives) which allow multiple network users to store files over a TCP/IP network. They are sometimes called a NAS box, NAS unit, NAS server, or NAS head.
NAT – Network Address Translation
This technique is used to help alleviate the limited number of IPv4 addresses. NAT was originally intended as a short-term solution to alleviate the shortage of available IPv4 addresses until IPv6 would be the common protocol, which has not happened. NAT is a method of having multiple non-unique, private IP inside addresses sharing one public IP address. By using NAT, devices on a private network can communicate with devices on a public network without the need for each device to have its own unique IP address. NAT uses port numbers to aid in mapping from internal (RFC 1918) IP addresses to globally unique, routable IP addresses. The future is IPv6 that has a large enough address field to give a unique IP address for every 1 square inch on the earth and more.
NBAR – Network-Based Application Recognition
A Cisco application that is an advanced application recognition engine for servers that utilize several classification techniques and has the ability to quickly update its classification rules for access and control. It uses Deep Packet Inspection to determine which traffic category the data flow belongs to. Used in conjunction with other features, it may then program the internal application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) to handle a specific flow and add security for “REAL” data flows.
NETSCOUT
NETSCOUT provides state-of-the-art solutions that help minimize disruptions by monitoring and trending network traffic for Internet circuits and VPN gateways. This includes metrics for traffic volume, dropped packets, and errors to provide early warning of potential and aberrant issues. Also, many attack prevention and mitigation capabilities – i.e., Ransomware, DDoS and other attacks,
NetFlow
A network protocol developed by Cisco for collecting IP traffic information and monitoring network flow. By analyzing NetFlow data, you can get a picture of network traffic flow and volume.
NFV – Network Function Virtualization
This technology employs inbuilt kernel features, re-extended Berkeley Packet Filter (eBPF) to fast filter and make decisions on every packet to pass or delete in the layer 2 environment. This implementation saves both system resources and network and decision latency, which is the largest issue in Autonomous DPI-like filtering systems.
NGFW – Next-Generation Firewall (leveraging DPI for advanced network security)
These Firewalls are much smarter than previous versions and can implement protection through Layer-7 of the OSI model. They also have many and MUCH smarter features and deeper threat recognition visibility with greatly expanded action ques with higher-speed recognition.
NIDS – Network Intrusion Detection System
Promiscuous, inside network systems that only “sniff” the traffic looking for issues and protection policies. Another part of NIDS are the Reporting and Alerting pieces.
NIPS – Network Intrusion Prevention System
A network security tool or solution that monitors the network 24×7. It works by recognizing, preventing and interrupting aberrant network events, attacks and controls behavior. These are very complex solutions that when added to DPI solutions and Firewalls can help prevent network damage, breaches, malware and MUCH more!
NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology
This Team is under the U.S. Department of Commerce and is one of the Nation’s Oldest Physical Science laboratories. NIST is charged with setting standards in place to promote U.S. innovation and protect the citizens of the U.S. NIST has set many standards which include a Cyber and Network framework of standards and rules designed to protect networks and the data within.
NPM – Network Performance Monitoring
This is a set of methods and processes, along with access equipment, to monitor a network’s performance levels through the collection and analysis of network traffic and network components like routers, switches…etc. NPM can also be used to recognize network users’ aberrant behavior and potential outsider access!
NTP – Network Time Protocol
This application by David Mills (1981) runs under UDP and provides universal network time synchronization. This application synchronizes with Stratum 0 atomic and GPS clocks to unify date and time stamps on all data packets and flows to under100ms.
OSI – Open Systems Interconnection
A conceptual model from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that describes the common seven layers that computer systems use to communicate over a network/Internet
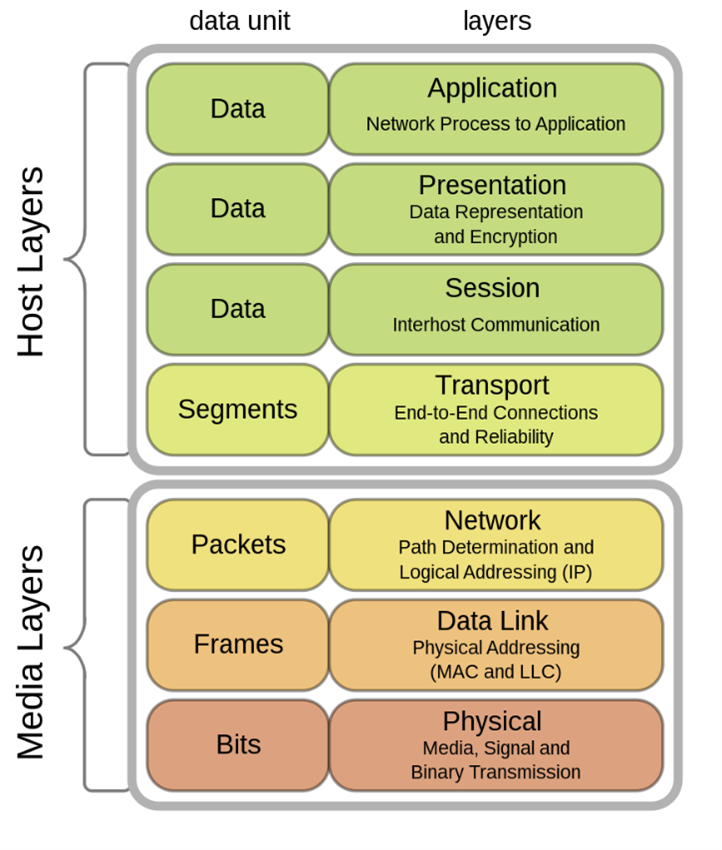
Graphic courtesy of Wikipedia “The Best Knowlege Place”
OSING – Open-Source Intelligence Techniques and Tools
This active research collaboration focuses on collecting (Passive), analyzing (Active), and disseminating information (Active) that is publicly available and legally accessible relating to cybersecurity and other areas of public concern. OSINT is used by organizations, including governments, businesses, and non-governmental organizations. It is useful in information gathering for a wide range of topics such as security threats, market research, and competitive intelligence…etc
OSPF – Open Shortest Path First
This Open Standard RFC – 2823 – is part of the Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) group. This link-state routing protocol first uses the Shortest Path First (SPF) or the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the best route for each packet flow method. Devices running OSPF protocol must establish neighbor relationships (Neighborhood Tables) before exchanging routes but not tables. OSPF devices have 3 important tables for best effort direction of packets, The first is the neighborhood table, the Topology table – the Topology of the internal networks involved, and the routing/forwarding tables – the best-known route that has been successful.
P2P DPI – Deep Packet Inspection for Peer-to-Peer traffic
A protection and monitoring method for P2P data flows. To use DPI focused for real-time data and analysis of packet contents for stateful protocol identification, flow monitoring, application monitoring, session monitoring, policy enforcement, use and usage control, quality of service, security, traffic management, and similar data protection functions.
PA – Packet Analysis
PA involves the inspection and examination of individual network packets to understand network behavior, troubleshoot issues, and gain insights into network performance, security, and protocols. It includes analyzing packet headers, payload, timing, and the relationships between packets to detect anomalies, diagnose problems, and optimize network performance.
PaaS – Platform-as-a-Service
A service in which cloud developers rent or are provided by the cloud provider everything that is required to build needed applications. They basically are relying on their cloud provider to offer the correct development tools, infrastructure, and operating systems. This is one of the three service models of cloud computing. The three models of cloud computing are PaaS (above), SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) which refers to full applications that are hosted in the cloud and maintained by the SaaS vendor and IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service), which refers to cloud computing infrastructure and access to servers, storage, etc. which are managed by their cloud vendor.
PACE – Packet Analysis and Content Extraction
Where one uses a packet monitoring, capture and analysis system to visualize and analyze their network flows by packets and metadata. The devices must be able to capture packets and allow for the extraction of data for deep data analysis including performance. Open-source packet capture solutions are very limited in access speed, have no way to address loss or dropped data and can-do limited extraction. Few devices can extract Metadata, automatically analyze performance, find and capture aberrant data, record data leaks, do network forensics, Real Data Extraction and much more like NETSCOUT’s Sniffer and nGenius solutions or WireShark.
PAF – Packet Analysis Framework
A data capture and analysis architecture that has100% visibility of ALL data, aberrant behavior recognition, performance details and storage solution. This may also include Deep Packet Inspection devices, as well as the diagnostic capability.
PAM – Packet Analysis Module
MUST be included in any PAF solution as the real-time, 100% data analysis piece.
PAT – Port Address Translation
Another method of address conservation like NAT – Network Address Translation. PAT permits multiple devices on a LAN to be mapped to a single public IP address by using port numbers. PAT plus NAT can add many extra levels of address safety and reduce internal address exhaustion.
PCAP – Packet Capture- A File Format for storage of Captured Packets
This file type contains packet data captured by a network monitoring tool and is used in post-analytics of the recorded network characteristics, dynamics, and much more. PCAP files are the most common storage format for data files but are only as accurate as the tools recording them. If your tool cannot capture and store full duplex high-speed data then the files are useless. Garbage in, garbage out! Computer-based software is only good for network speeds of less than gigabit rates.
PDU – Protocol Data Unit
In networking, a PDU is a single unit of information transmitted among peer entities of a network at a given layer of protocol. Every protocol has its own PDUs. It carries the protocol-control information and/or user data. The PDU is the unit of exchange between communicating entities. The PDU is the envelope of the carried data or control information.
PDU – Power Data Unit
Another type of PDU is a device for controlling provided AC electrical power in a data center. The most basic PDUs are power strips with or without surge protection.
PNT – Positioning, Navigation, and Timing
PNT is necessary for the functioning of the nation’s critical infrastructure. All communications use PNT standards for everything from Internet to monitoring systems, etc. Whether for civil, commercial, or military use, nearly all sectors rely on accurate PNT information to provide services definitions, as there are MANY types on PNT.
PoE – Power over Ethernet
Any of several standards and/or ad hoc systems that pass electric power (DC) along with data on twisted-pair Ethernet cabling. The delimiter is that PoE cannot power high-end machines like routers, switches, etc., and in some conditions the power transfer causes noise that can seriously affect the data integrity. Powered Devices (PD) are small power demand devices i.e., IP phones and IP cameras. IEEE 802.3af, also known as standard PoE, operates at a voltage range of 44-57V and supplies a current of 10-350mA. In this standard, the maximum power output of a port is limited to 15.4W. Distance is another limiting factor in using PoE.
POP – Post Office Protocol
Originally released as a standard of Internet mail in 1984 it has been updated to POPv3. This is the Internet standard that allows one to download email messages from an email server to a computer cell phone, notebook, etc.
POTS – Plain Old Telephone Service
Sometimes referred to as PSTN or public switched telephone network. These were hard-wired (twisted pair copper wired) voice-grade analog telephone communications through hard-wired handsets.
PPP – Point-to-Point Protocol
The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) directly connects two network devices to two networks at the data link layer using transport connections like ISDN, and DSL through a Wide area net.
PPTP – Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
A mostly obsolete technique for implementing virtual private networks on port 1723. It had many data protection issues and is not used much.
PTP – Precision Time Protocol
This IEEE standard 1588-2019 is known as version V2.1. This timing protocol is accurate up to less than a microsecond and is usually measured in nanoseconds – .000,000,001 seconds where NTP is accurate, under ten milliseconds – .010 seconds. PTP is used to coordinate time sensitive environments, like stock trading and manufacturing, where timing is important with IoT and IIoT robots in production lines and streaming environments like video conferencing where voice and video must be coordinated.
QoS – Quality of Service
In networks, QoS means regulating network resources in the degree of packet loss, network jitter and latency, plus the overall performance of cloud, or computer network services and the tools/technologies that guarantee the network’s ability to run high-priority operations. There are three general models used when applying Quality of Service (QoS). These are:
- Best Effort – No special needs – No QoS needed or requested
- DiffServ Differentiated Services – QoS is implemented on a “hop by hop” basis where we use the ToS byte of IP packets for classification needs
- IntServ Integrated Services – A signaling process, like RSVP where network flows can request a certain bandwidth, delay, etc. that is required for the flow
This is especially important in automation control environments like IoT and IIoT.
RADIUS – Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
Usually used with the IEEE 802.1x authentication standard. This is a client-server networking protocol that facilitates communications between a central server and individual users who want to gain access to the network access server (NAS). The NAS then verifies the user’s information through the RADIUS authentication server. The authentication information may include details, such as a username, a password, and an IP address, etc.
RARP – Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
An obsolete computer communication protocol used by a client computer to request its Internet Protocol (IPv4) address from a computer network. It has been replaced by BooTP and DHCP.
RDP – Remote Desktop Protocol
This Microsoft protocol was developed to allow a host computer to connect and control another remote computer through the network to help fix Windows issues. RDP is sometimes called Windows Remote Desktop or Windows Terminal Server and is among the most commonly exploited access for ransomware and malicious attackers. It is a very dangerous access and remote-control technology and should be removed to help stop this as an attack origin which requires open ports on a public address that can be highly dangerous!
RIP – Routing Information Protocol
RIP uses a single routing methodology to measure the distance between the source and the destination network. RIP is a classless routing protocol that is capable of advertising subnet mask information and uses multicast to send routing updates. RIPv2 sends the entire routing table with updates every 30 seconds. RIP is mainly used on small networks because it is very simple to configure and maintain but lacks the advanced features of other routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP.
RSTP – Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
This IEEE 802.1w standard is an advancement over STP and follows a strict set of rules by which the switches decide the best way to forward the traffic on the network free from any redundancy, preventing bridge loops and broadcast storms and allowing for the rapid recovery of failed links in a network. It is a complex improvement and is backward capable to the STP standard. It has been revised many times, thus adding to its complexity.
RSVP – Resource Reservation Protocol
This protocol requests for a certain level of QoS, delay, bandwidth, jitter, or services end-to-end, which is mostly controlled by the routers in a network. Admission Control is used to permit or deny the request. Once the communication is complete, the resources are released. RSVP conforms to the QoS model definitions and standards.
RUM – Real User Monitoring
RUM is a performance monitoring process that collects detailed data about a user’s interaction with an application. Real user monitoring collects data on a variety of metrics.
SaaS – Software as a Service
A subscription-based application that is accessed remotely and may also be called Web-based, On-Demand or Hosted software.
SAN – Storage Area Network
SAN’s are rapidly becoming the most common storage architectures used by enterprises. SANs allow for business-critical applications that require high-throughput and low-latency shared storage. This allows for consistent modalities and other cyber security processes with methods to meet today’s security, data protection, and recovery requirements.
SASE – Service Access Sever Edge
This cloud-based solution converges network and security functionalities into the cloud and or corporate SD-WAN functionality which offers network optimization, the integrated security stack may include Next Generation Firewall (NGFW), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), and more – secures traffic over the corporate WAN. Gartner (who coined this in 2019), SASE is “the future of network security.”
SAT – Security Awareness Training and CyberSecurity Awareness –
Both are focused on training all Staff to recognize, report, and neutralize network attacks and to help avoid security incidents both direct attacks as well as Phishing and social engineering attacks.
SDN – Software-Defined Networking
A newer technology that allows one to manage a network through software. Network managers can configure, manage, secure, and optimize their network resources very quickly through software, allowing them to meet their current physical network needs or the control plane of the network.
SDNs are operated through devices that manage packet processing through efficient software-based encoding rather than through more conventional programming methods. P4 is a language used, e.g., by OpenFlow SDNs.
SDP – Session Description Protocol
This SIP data unit is used to specify the transferring media format, the codec, and protocol where the voice and video streams are carried by RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) or SRTP the secure version of RTP.
SDU – Service Data Unit
SDU is the data or control information carried to a device or user using the PDU. See PDU! Theservice data unit(SDU) is the unit of data to be delivered over data networks. The SDU can be thought of as the message to be delivered by the next lower protocol layer – the PDU. See also PDU – Payload Data Unit.
SD-WAN
Software Defined Wide Area Networks – A large WAN network that is configured, managed (i.e. controlled) and protected without hardware.
SEG – Secure Email Gateway
SEG’s focus on stopping BEC’s using signature analysis and machine learning to identify and block malicious emails before they reach inboxes. This technology is very important because email attacks, such as phishing, are some of the most common and costly cyber threats organizations face today.
SFTP – Secure (SSH) File Transfer Protocol
This secure FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used to provide file access, transfer and management securely using the SSH and FTP protocols.
SIEM – Security Information and Event Management
This solution is designed to Detect, Analyze, and Respond to recognized security threats. This is usually a combination of SIM (Security Information Management) and SEM (Security Event Management) into one solution to recognize rapid threats and cyber-attacks to best meet compliance standards. It can also include AI to make it better and faster.
SIP – Session Initiation Protocol
A layer 7 protocol used for initiating, maintaining, and terminating voice, video and messaging Internet telephony communication sessions. It is also used in LTE
SLA – Service Level Agreement
An agreement/contract between customer and provider with the parameters of service and measurement methods.
SMB – Server Message Block
This protocol enables the sharing of network elements like printers, files and other inter-process elements.
SMTP – Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
This protocol is used to manage the transfer of Internet mail between senders and receivers.
SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol
This application layer protocol is used to monitor and manage network elements i.e., computers, routers, switches, etc.
SOAR – Security Orchestration, Automation and Response
This is a stack of Software Applications that enables an organization to capture and collect relevant data with many tools i.e. Firewalls, Scanners, and SIEM platforms around cybersecurity threats. The goal is to allow for action-based responses to security events with little or no human assistance.
SOC – Security Operations Center
This centralized area is focused on threat detection, mitigation and recovery.
SPCA – Sequential Parametric Convex Approximation –
A method for WiFi using the MIMO method of data transfer where we must consider the (global and sum) energy efficiency optimization problem in downlink multi-input multi-output multi-cell WIFI systems, where all users suffer from multiuser interference and WIFI hacking. We must develop and deploy an algorithm for multi-transmitting and Multi Receiving interference efficiency. 5G and IoT, IIoT wireless connections will reach over 500+ billion devices WW will cause wireless interference without some new methods of accessing the Internet. SWIPT is one such method!
SSCS – Software Supply Chain Security
A strategy by which supply organizations detect, identify, analyze and/or mitigate associated risks and attacks within the supply control plane using the monitored digital signatures and artifacts within the supply network. This strategy combines risk management and cybersecurity principles to assess supply chain risks and implement measures to block, mitigate, or remediate issues no matter the origin, inside or outside the supply chain network.
SSE – Security Service Edge
(Gartner Definition) – a solution and process that secures access to the web, cloud services and private applications. Capabilities include access control, threat protection, data security, security monitoring, and acceptable-use control enforced by network-based and API-based integration. SSE is primarily delivered as a cloud-based service, and may include on-premises or agent-based components. SSE is considered a subset of the (SASE) Secure Access Service Edge framework. SSE can include Secure Web Gateway (SWG), Zero trust Network Access (ZTNA), Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) and also Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS)
SSH – Secure Shell
An IETF standard is for encryption communicating over an unsecured client-server environment-based network. It is mostly used for remote login (User Name and Password authentication) to establish a secure connection between computers, servers, and browsers and for command-line execution within the connection. Note: SSH also refers to the UNIX (Wikipedia definition) design to replace Telnet and for unsecured remote Unix shell protocols, such as the Berkeley Remote Shell (rsh) and the related rlogin and rexec protocols, which all use insecure, plaintext transmission of authentication tokens.
SSID – Service Set Identifier
The Identifier that allows for unique WiFi network naming.
SSL – Secure Sockets Layer
This is/was a cryptographic protocol used to authenticate Internet connections, but has mostly been replaced by Transport Layer Security, or TLS around 1999.
SSO – Single Sign-On
Allows users to use one set of network identification credentials to access several sites, databases, and other controlled access environments. Today, most security environments require at least 2 access credentials.
STP – Spanning Tree Protocol – IEEE 802.1D algorithm
STP is to ensure that you do not create network deadly layer 2 loops when you have redundant switch paths in your network and prevent broadcast storms. Switches exchanging BPDU messages with other switches to detect loops, and then removes the loop by shutting down selected bridge/switch interfaces. This algorithm guarantees that there is one and only one active path between two network devices.
SWG – Secure Web Gateway
A security solution focused on preventing unsecured Internet traffic from entering an internal network and enforcing corporate access policies to prevent web-based attacks and threats.
SWIPT – Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer
This new technology idea is focused on providing cost-effective information and energy access to wireless devices through transmit beamforming where multiple transmitter antennas are used to adaptively form transmit beams toward multiple information and energy user receivers to effectively compensate the path loss as well as mitigate the inter-user interference. This is currently an experimental technology!
TACACS+ – Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System Plus
A Cisco full-encryption protocol (broader than Radius, which only encrypts passwords) that encrypts all packets, thus providing control over the authorization of commands. TACACS+ requires access to an authentication server to validate users access to the network and the data.
TCP/IP – Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
A suite of data network communication protocols originally invented by Vint Cerf and Rob Kahn in the 1970’s used to interconnect network devices and computers on the Internet and in private networks. Much evolved since then, it is used to interconnect network devices and computers in multiple network environments. TCP/IP is used on the Internet and in private networks.
TCPDUMP (TCP Dump)
A command line (C) utility that allows one to capture and analyze network traffic using a computer. It has speed limitations, minimal analytics and limited visualizations.
TFTP – Trivial File Transfer Protocol
A simple non-authentication protocol that provides very basic file transfer. TFTP is not like FTP, which has sophisticated protection and authentication algorithms.
TLS – Transport Layer Security – RFC 6347
A cryptographic method that provides authentication, privacy and data integrity between two communicating computers
TPRM – Third Party Risk Management
This is a new third-party off-site Risk Management solution for companies that cannot or will not handle their Network Security and Risk Management internally. The lack of industry professionals and the cost for Security and Risk management solutions has led to this new and unproven industry segment.
UDP – User Datagram Protocol
A transport layer protocol for configuring packets to be transported/sent across data networks. TCP is a connection-based protocol and UDP is connectionless. Both ride over the IP layer of protocol.
UTM – Unified Threat Management (incorporating DPI as part of its security features)
Deployed at the network perimeter or edge. These devices scan all data in and out of the network. Using deep packet inspection (DPI), a UTM solution gains full visibility into all network packets to identify incoming threats and blocks dangerous web/user requests. UTM can provide a single dashboard for security teams to manage and update, thus providing the ability to rapidly recognize threats.
VIP or VIPA – Virtual IP Address
IP addresses that are not connected to physical machines or interfaces. These soft assigned addresses can rotate among nodes in a Content Gateway cluster. It is not uncommon for one machine to represent multiple IP addresses on the same subnet. When incoming data packets are sent to the VIP address, they are then routed to real, actual and factual network interfaces.
VIPS – Voice Intrusion Prevention System
This is a type of security management system for voice networks! This device monitors voice traffic for anomalous activity which includes multiple calling patterns, attack/abuse signatures, Denial of Service, telecom attacks, service abuse, and other attack modalities that may cause corporate voice corruption. See IPS herein!
VLAN – Virtual Local Area Network
VLAN is an overlay network that organizes groups of users/devices together that share a virtual LAN. The purpose is to isolate and deliver traffic to each device or logical group. i.e., a department, floor, campus, etc.
VLSM – Variable Length Subnet Masking
A method of utilizing IPv4 addresses by adding Subnet addresses. Subnetting is the process of dividing a single large network into multiple small networks known as subnets. The primary purpose of subnetting is to help relieve network congestion and improve efficiency in the utilization of the relatively small network address space available in IPv4.
VoIP – Voice over Internet Protocol
This involves IP digitized voice (analog) calls over a digital network. This protocol supports digitized analog signals over an IP-based network.
VPLS – Virtual Private LAN Service
A Multipoint-to-Multipoint Layer 2 VPN encrypted service that connects multiple branches of a Client, like a company group or department, in a single logical switched architecture over a service providers IP/MPLS network.
VPN – Virtual Private Network
A mechanism or tunneling protocol that creates a secure connection between computing devices and/or a computer network or between two networks. It is designed to hide communications and may use a variety of encryption methods.
VRRP – Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
VRRP eliminates the single point of failure inherent in the static default routed environment by managing L3 and routers creating redundant paths through the LAN network. See also HSRP.
VTP – VLAN Trunking Protocol
A multiplexing protocol that allows users to transmit many VLAN’s traffic as opposed to just one link at a time.
WAF – Web Application Fire
employing DPI to inspect and protect web traffic
WAN – Wide Area Network – Using TCP
Transmission Control Protocol using many LANs can communicate to other networks remotely. A network of networks i.e. the Internet. This includes many methods – Frame Relay, MPLS, and many more methods, but TCP is the primary today.
WAP – Wireless Access Point
A networking device that allows wireless-capable (WiFi) devices to connect to a wired network.
WEP – Wired Equivalent Privacy
A method to protect WiFi data by encrypting the data so outsiders who are not inside the encrypted network will not be able to read the messages or data contained within. An older method was WPA and the newer and safer is WPA2.
Wireshark
Open-Source Protocol Analyzer – Started as Ethereal by Gerald Combs – The best Open-source data packet capture and data analyzer!
WLAN – Wireless Local Area Network
A wireless network (using radio or infrared signals instead of traditional network cabling) that allows two or more devices to be wirelessly connected to form a local area network for access to the Internet or private network.
WLC – Wireless LAN Controller
A network device used to monitor and manage wireless access points in a network!
WPA – Wi-Fi Protected Access
A security standard to help secure computing devices equipped with wireless access to connect to the Internet. WPA was developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to provide more sophisticated data encryption and better user authentication than Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), the original WiFi security standard. WPA was initially released in 2003. The Wi-Fi Alliance defined WPA as a response to serious weaknesses found in the WEP protocol. A more secure version, WPA2, was released in 2004. In 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced the release of WPA’s third and current version, WPA3.
WPA2 – WiFi Protected Access II
Interval WiFi data security method.
WPA3 – WiFi Protected Access III
The latest security for WiFi devices to access the LAN network and data protection.
WPS – WiFi Protected Setup
WPS was originally called WiFi Simple Config. WPS is a network security standard to create a secure wireless home network simply and easily. Created by Cisco and introduced in 2006, it was designed to make it easy to add new devices to an existing WiFi network without entering long passphrases.
WWAN – Wireless Wide Area Network
WWAN is a network connection used in conjunction with mobile communication technologies, such as WIMAX, CDMA, and GSM. Any user with a WWAN card can connect to and access the Internet. WWAN uses 128-bit encryption and is very secure.
WWW or W3 or just the Web
World Wide Web – is part of the Internet and founded by Tim Berners-Lee and is the leading information service on the Internet. If you search the Internet, you are using the WWW.
XDR – Extended Detection and Response
XDR is a monitoring strategy/method which allows for monitoring data flows in networks from endpoint devices to firewalls, to cloud activities and third-party applications. XDR identifies incidents and threats across the environment and collates related occurrences, optimizing the number of security alerts and allowing security teams to understand a cyberattack more clearly.
ZTNA – Zero Trust Network Access
This network security solution provides secure remote access to the corporate network’s applications, data, and services based on VERY clearly defined access control policies. Only specific users can access certain applications and/or data and only after stringent authentication.